Knowledge management: Key findings and lessons Marcelo Hoffmann. 1.* Okay, thank you, Doug. Okay. So what I will do today is give you a very, very short run-down of knowledge management in the business environment. It will be a very short. 20-minute, or so, presentation. And take it with a grain of salt; it's meant to be for business because those are our clients. But the meta-lesson from this, if you will take it, is how does this relate to bootstrapping? How does this relate to the government, or NGOs, and so on? We'll have Peter Yim speak afterwards about an NGO and what they do, which in a sense are a type of knowledge management. But my bias will be directly related only to companies because that's the environment where I work. Okay, I have to move this to get-sorry, presentation on the left there?
Okay, thank you.
So, with that, the concept is nothing new. It's been around for a long
time. Different authors have taken different perspectives on this.Doug
has presented his views. Peter Drucker has written extensively about knowledge
workers. But what is new now is the internet. It is the networks; it is
the greater computing power and the like.
We can say that the status is pretty much equivalent to the quality movements of 20-30 years ago when you speak about knowledge management in the corporate settings. Everybody speaks about knowledge management as if it were something consistent, unique, individualizable, et cetera; it is not. And I will give some descriptions of what different folks mean by knowledge management and then talk about some cases, some suggestions for implementation, and then what we see in the future. And then, perhaps, if you will, keep in your mind how does this relate to Doug's ideas, theories, strategies, and the like. One thing I would like to emphasize: that this knowledge management stuff is not a fad. It's definitely something that will remain for a while, but it will evolve. The popularity has been only in the last five years. It probably might change in terms of methodology, syntax, semantics, and the like, but it's not going to go away as some of the other business consulting fads have come and gone. Perhaps something to keep in mind also is what methodologies are applicable to be transferred from the mileu of knowledge management to bootstrapping. I believe some will, some will not; but perhaps it's something we should look at collectively. For lack of a definition there are many descriptions, but one thing
that is very consistent is something about value; either creating value,
or reusing value, or conversion into or out of value, reuse of knowledge
and the like.
It's a result of many evolutionary processes and trends. But, definitely,
it's mostly about management. When you really get down to it, if you cannot
manage a corporation you're not going to be able to do knowledge management
particularly well. And, I'll get into that in greater detail later on.
The practices vary. And, these I would like to emphasize. Different writers, different authors and consultants speak as if knowledge management were any one of these four components; and sometimes a mix, combination, hybrids, and the like. But all these are included by some anyway. Valuing knowledge has been around for a while, getting increasing importance in terms of recognition and evaluation. Evaluation is very problematic. There are some attempts to go beyond accounting, but it is a matter of judgment. There are no ways to measure and value knowledge in a unique, repeatable way. But there's some ways in which you can compare greater or lesser value. Exploiting intellectual property, that's something that's very much in vogue, particularly by large companies that have been able to reduce the cost of maintaining intellectual property -- selling what they have that they're not using -- companies like Dow and Motorola. There are a number of cases where they have used this very effectively, both to reduce their cost and increase their profitability. Managing knowledge workers, that's been around forever, perhaps since the Middle Ages, but obviously it's getting more and more important now. And I will emphasize this later on in my presentation that, if there is a meta-message behind this knowledge management fad or movement, is that what is being used rather effectively is what's considered explicit knowledge, stuff that falls into databases, knowledge bases, manuals, you know, all the stuff that's very obviously valuable, and useful, and repeatable, and reusable, and so on. What isn't well used, or not as well used, is what's tacit, implicit in people's heads, that sort of thing. We haven't quite learned how to reuse what's in people's heads. But I'll give some suggestions of technologies that might help reduce the problem of reusing implicit knowledge. The last one is the one that perhaps has the most potential, the greatest value, and arguably, the most difficult to capture. This whole issue of capturing - I will read it directly - sharing/distribution of work-based learning from the day-today work of knowledge workers. And this implies from within the firm, outside competitors, suppliers, allies, and the like. This is very problematic, and for this you would need to have something like what Doug calls a dynamic knowledge repository. What we have seen in the companies we have studied is that this is not done particularly well. It's done very ad-hoc. Some companies will bet on others, but perhaps by chance, or by cultural reason, there is no great methodology that can be transferred. And the practices of the four components that you see above here do overlap, and at times, keep expanding. Now when looking at the approaches, the formal approaches used by companies
who are very heavily involved with knowledge management, evolve. The first
movement, if you would, of keeping track of repositories has been pretty
much done by most large companies. It's fairly straightforward; it's not
that difficult to do.
And you see all the different kinds of collections of knowledge, or information, or data, if you would. But the latter component, which we think is very important, is relatively new: the whole thing about search engines, data-mining, visualization, making stuff available more easily, making stuff available when people need it, ideally as they need it. That's a little bit of a stretch as of now, but perhaps in time. Technology solutions are coming. The second set of activities; the second set of approaches is this whole
arena of networks. And that's for the purpose of creating, holding, transferring
tacit, or implicit, knowledge. This is much more problematic. It's really
about managing people, deciding organizations, evolving organizations and
the people who are within them.
Different companies use different approaches. The classic ways are connecting people, teams, ad-hoc get-togethers. Some of the better companies locally, you can see they design their offices and their buildings to increase the likelihood that people will meet with others. Several folks here who have worked for Sun will smile when I mention that at the new Sun facility in Menlo Park there are like mini-cafeterias every so often as a way to have folks gather there, exchange information, knowledge. And, surprise, surprise, there are whiteboards right across there. Well, it is to get this exchange that cannot be done in other, more formal ways. And the last point about communities of learning and practice is something that has been going on now for a while, but increasingly there is more attention to this. And I think that as the technology to connect on the networks, which has become increasingly more powerful, this will become even more popular. However, face-to-face will not go away any time soon. If there's a question about this, perhaps there might be competition with very high-definition screens, and so on, if you can get the dynamics that are better than being there. But I'm not sure that that will be the case. Not yet, not for a while anyway.
If we look at the enablers and resources that are used for knowledge
management-you can go from the left side, going from noise, data, information.
I spoke about knowledge as object, then going on from knowledge as process.
The higher, right-hand corner will be knowledge as emergent properties.
And this is really tricky to go to. That's something that I believe is
still a research question. Perhaps by using bootstrap in evolving organizations
beyond the current state, this will work out. But there is no methodology
approach that I know of for all the companies I've interviewed, and visited
with, and spoken to. But, in a sense, there is this transition from the
low-end stuff to the higher-end, increasingly more tacit, and more complex,
and much more difficult to transfer.
The emphases, by various companies, vary dramatically. If you look here, from the left side, the more mechanistic approaches to the organic. If there's one message that we can convey it's that, in general, most modern companies are going from the left side to the right side, but not all evenly and not evenly down this list of characteristics. One company might be very interested in short-term tactical ideas, but very involved with creativity and innovation, and so on. So, you would see somewhat of a zigzag of organizations if you were to take some sort of measurement across a large number. But, in general, we have seen a transition from the left side to the right side, towards more biological approaches-and also larger-scale, and more chaotic, perhaps going along with, the Santa Fe Institute talks about that, chaos and chaos theory. Another way of looking at this knowledge management and the processes underneath is that they tend to go from the simple/tangible on to the less tangible, but potentially the greater the benefit.
Another way of looking at this knowledge management and the processes underneath is that they tend to go from the simple/tangible on to the less and less tangible, but potentially the greater the benefit. And, when I've given these presentations in different companies and different companies, what tends to come back from the dialog is most companies are at the left-hand corner, bottom left-hand corner; trying to avoid repeating the invention of the wheel. And they keep doing that, over time, more efficiently. Some are going to the concept of how do they make a better wheel; but not that many, and not often on purpose. If this were drawn to scale, there would be a major chasm between that and the fellow on the hand-glider, because that's changing paradigms. That's very difficult-going from there to thinking about thinking. The meta-approaches that Doug proposes, I have yet to see any organization, any other speaker, besides Doug and the group that's promoting and trying to bring this bootstrapping to happen, suggesting this. So, if there were a chart describing where the companies are that we have observed, it would be largely at the bottom left, with a few going up, and then nobody at the top, right-hand side. And, there might be some hypotheses about countries, and size of organization, and so on. Going back to, say, some visits in Japan some time back-Japanese companies, for example, are very good at not re-inventing the wheel. They transfer that kind of knowledge relatively well. They have a very hard time with creativity and innovation, and so on. Different cultures will work differently-better for some things, less well for others. Organizational models are something very important to look at for considering knowledge management.
The three kinds of organizations, for lack of a better taxonomy that
we have seen-command-and-control, exchange economy, and gift society. What's
very common is that many speakers present the idea for gift society as
if that were the one that they would get to first. I have yet to see that
happen-if anything, you can get into exchange economy where there's a trade
off: I will give you something if you will give me something in return
that's equally valuable or better. And one of the suggestions we make is
to go for that, to go for the exchange economy. Don't assume that you will
generate a gift society or a gift group just by itself. You have to develop
the trust-go from command-and-control to exchange economy and then to a
gift society. And, in fact, most organizations will probably oscillate
between an exchange economy environment and a gift society environment.
You know, depending if the trust goes up and down. But, it's still better
than working in command-and-control where folks will only contribute what
they have to contribute, and no more. So, this is something to consider
if one were to analyze what is the situation in a particular company and
we suggest to also consider how to ferment the evolution from an exchange
economy to a gift society. What we have found among the cases that we have
analyzed in greater detail is that they're extremely contextual to be successful.
There's no generic approach that will work in different companies.
There are two cases that I have found that are classics: Chaparral Steel,
a small mini-mill, some couple thousand people, and Boeing, the triple
seven-I just couldn't think of Boeing as a company because it's just too
large. But if you can compare Chaparral Steel, they work essentially as
if they were a company working in the Middle Ages with apprenticeships.
And they have their R&B on the production floor, so newer folks learn
from people who have been there longer and who have done steel-making longer,
and so on-very tacit knowledge. Very little use of computers. Once they
sell the steel, it's gone; they don't have to guarantee it anymore. If
you contrast that to Boeing where they have to keep track of everything
they've done for years and years, maybe for 40 or 50 years after the airplane
will fly, it's a very different environment. It's a different approach-and
for good reasons. So if I were to take another metaphor-it's sort of right-brain/left-brain,
but the whole concept here is to be specific. What kind of organization
do you have? What do you want to get out of it? And then, what do you decide
for it? Perhaps, what sort of folks do you hire, train, support, that sort
of thing? One of the suggestions we have found is very useful is, go for
the early benefits. There's nothing better, to build up the bandwagon effect,
than being successful early on. And what we have found within that is the
idea of going after improved knowledge repositories.
It's much easier to prove the benefit of these than to prove the benefit
of a network that might take six months, a year, two years to come up with
something interesting and exciting. Also, going for effectiveness and efficiency,
and even though these may be lower-level gains, they're still useful to
create the environment that, in a sense, will take you to a higher-level.
But one thing to keep in mind-you cannot predict what will happen in the
longer run. Literally, users build the road as they travel it; and it's
a co-discovery between the developers, the designers, participants, and
the like. It's an interesting travel with all kinds of detours. Some of
the risks that we have found in organizations that try to do this fast
is shifts in power, the changes in politics and relationships and so on,
were very problematic. And, often times, the senior manager was not aware
of what the effects would be until after the fact, until it was a major
crash.
And, the problem of implementing this things is also difficult enough
that we suggest: start small, evolve, grow, see what works in your organization,
and then, as long as there are successes, things will evolve nicely. Otherwise,
if you try to do something big, there will be major problems in allocating
costs because those who pay are not necessarily those who benefit. Then,
there will be a major fight for who pays, who gains, where, when. In addition,
these things spread over time, which is very problematic because there
is still-as I mentioned before--not very good ways to measure what the
value of improved knowledge management will be over time. We have found
that there are at least two kinds of resources that are absolutely crucial.
The organizational part, in Doug's terminology, would be the human systems,
the agreements, the excitement, and he commotion of the right kinds of
activities, of behaviors, that sort of thing. We would add mentoring, training,
support to the point of being pedantic.
Definitely leadership from senior executives is very important.
Besides that infrastructure, I will go back to what I mentioned earlier:
even the architecture of the buildings where collaborators work is important-for
folks to meet in an environment that's conducive for them to do what they
want to do, better. Obviously, computers, networks, all that, they are
nice, nothing new there but important to have ongoing mentoring, training,
and support. We have had cases of that, even at SRI, where as Microsoft
keeps changing the software, we need support where we didn't think we would
need support. So, I've had several cases of that myself.
Several things that we see as enablers now that also I mentioned earlier-about
the networks, the tools, the internet-a lot of value will be gained from
the transition from HTML to XML, perhaps KQML, Java, others. I think we'll
have some speakers later--next week and the following week-getting into
this in much greater detail. So, I will not dwell onto this one. Search
technology is going to be very important because soon there will be the
ability to capture, as Jim Spohrer said last week. You know, if you can
have a very small form factor hard drive that can store all the audio for
your whole life, well that's nice, but then how do you find anything. So,
if we have better search techniques and approaches, particularly things
from artificial intelligence-speech recognition, natural language, knowledge
bases, and so on-in a somewhat automated fashion. That'll be quite nice
and useful. These things are here now; they can be used better, but they're
there. Okay, one thing that's coming up, that's not quite there yet, the
idea of cross-referencing multi-media-actually SRI has some efforts on
this where you can cross-correlate different media streams from video,
sound, documents, and so on. And, if you can do what amounts to a multi-media
search, there's a great potential there-both for good and for spying, and
for privacy violations, and for security problems. But still, it's something
worth looking at because it's got very good potential. This whole idea
of automating some of the activities that people do now also has huge potential,
although it will never, or not for a long time, become completely automated.
I don't think people will be pulled out of the loop; but, perhaps the lower-level
activities, thee lower-level tasks, can be automated. I believe Doug goes
along with that in terms of co-evolution and so on. The suggestions that
we have made that seem to be consistent with most of the success cases
that we've seen follow here.
The idea is to start looking at what are the needs. Take a very gook
look at the human organizational elements, factors, environment, culture,
all that. Then start the design process with the knowledge architecture.
What should be the ideal combination of things so that users would get
benefits fairly early on? Only then think of the technology infrastructure,
and then stop. Start doing this in modular fashion: test, improve and repeat
the steps. This is a highly intricate process. I have yet to see any successful
company deploy a formal, large knowledge management system in one fell
swoop. It just doesn't happen; it's too complicated.
Some of the possibilities ahead include: the processes in a much more global fashion--large scale implementations, what Doug talks about, you know, meta-meta levels--large organizations collaborating in a closely coupled fashion, maybe across countries or large enterprises. Another great opportunity is the one to enhance individual and group creativity. That's something we don't have much of a handle yet, but perhaps by reducing the lower-level functions then perhaps folks will have the time and ability to do the higher-level activities. And then, this whole notion of this seamless web of resources combining them in a fashion that is useful at the time that has needed, in the best way. That is a little bit of a pie in the sky for now, but perhaps not in a few years. It is something that we will have to evolve into. And, I want to finish with some comments on a slide presented by Jim Spohrer last week about learning that although when it comes to knowledge management it has taken, to some extent, the first three of these components, performance support, practice skills, habits, and training. It has yet to, within the corporate setting, look at education, research, the finding of new answers and the finding of new questions. There's still a lot of opportunity there, but I'm not sure that we quite have it yet. And, with that, I finish my presentation and cede the floor back to Doug. Thank you.
---
Above space serves to put hyperlinked
targets at the top of the window
|

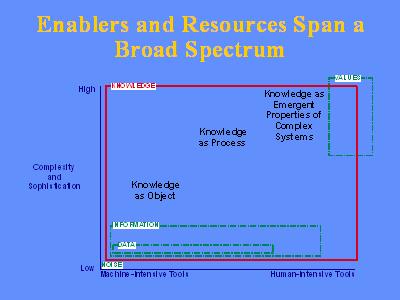 Fig. 1
Fig. 1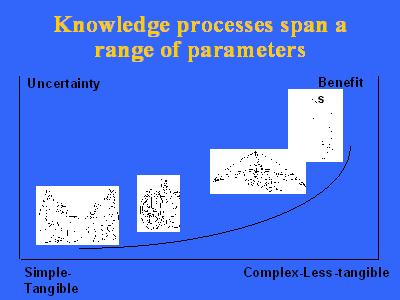 Fig. 2
Fig. 2